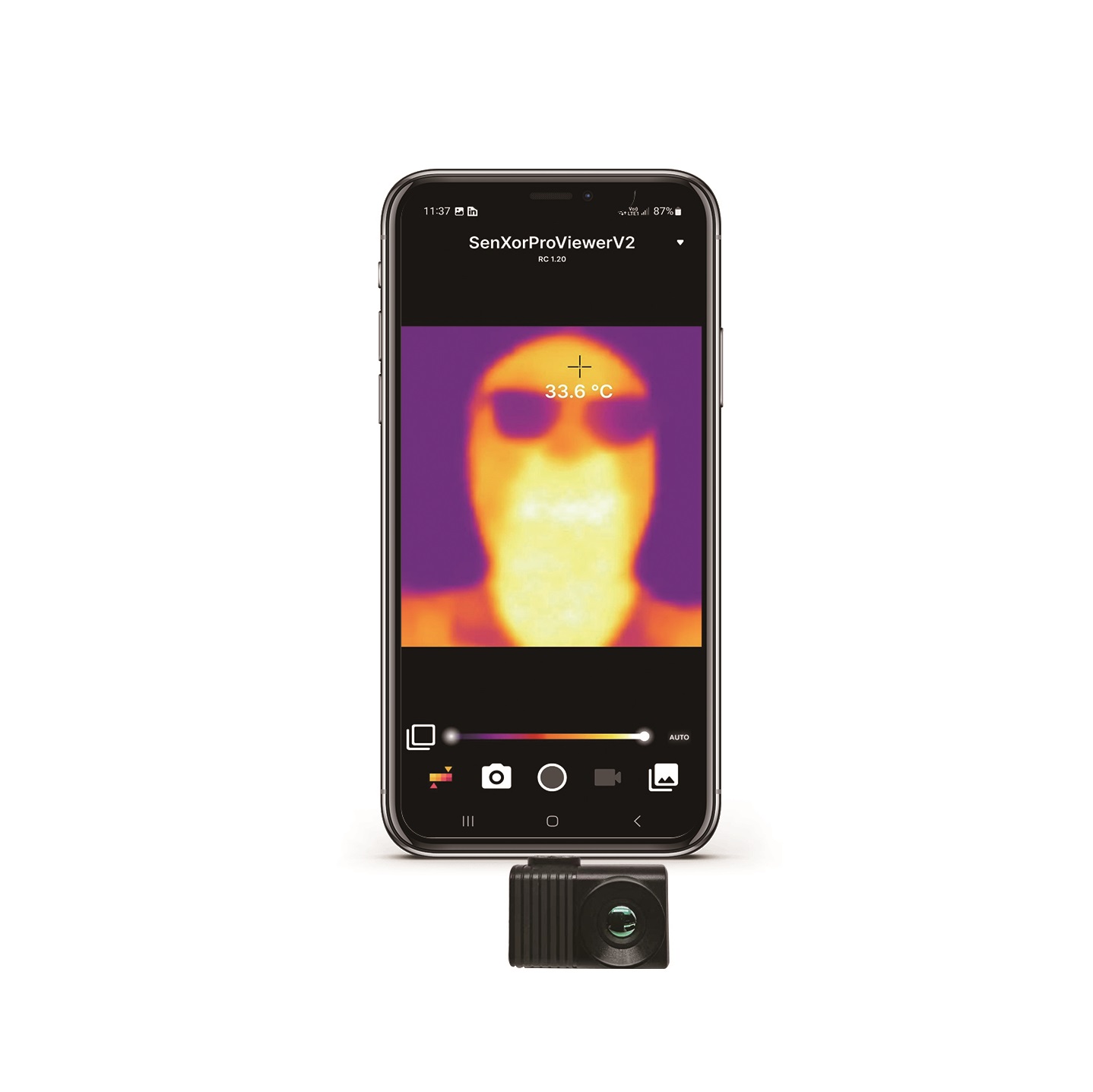
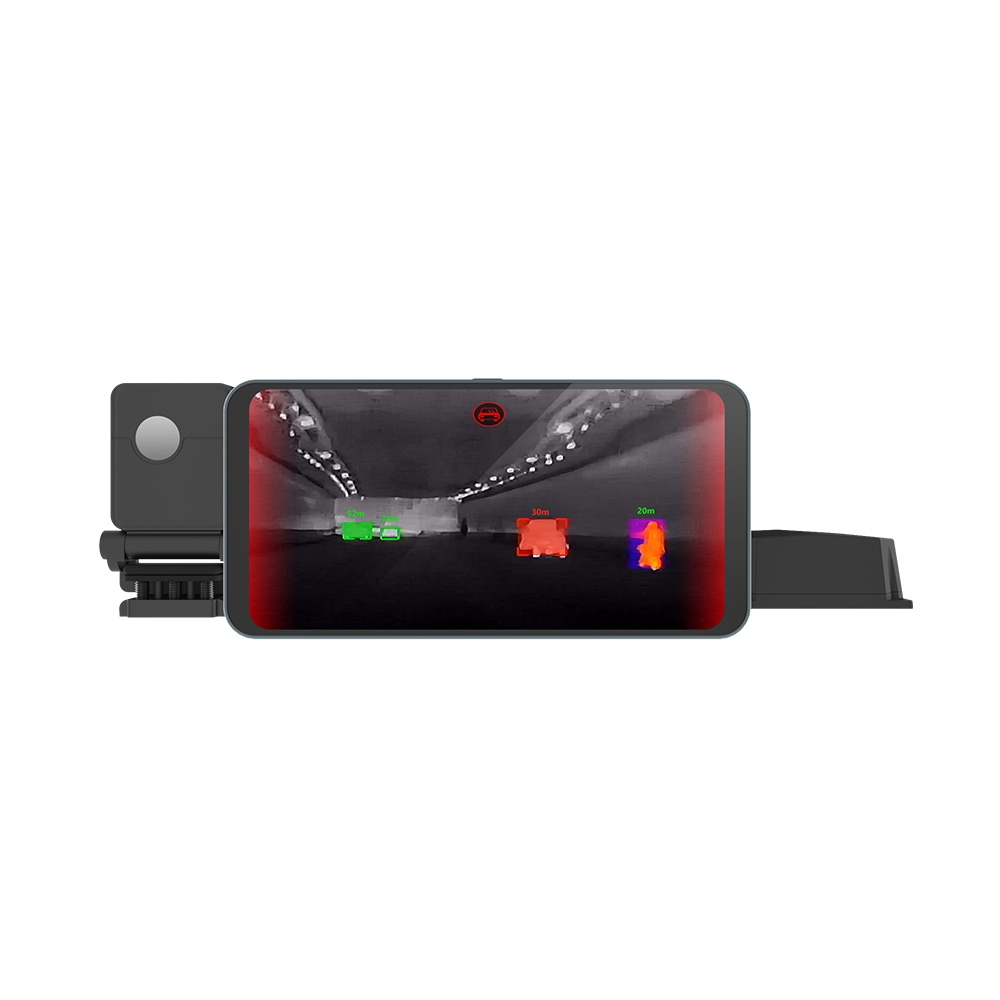
How to Detect Transformer Faults Effortlessly: Thermal Imaging Guide for Industrial Standards
2025年7月14日RS300 Thermal Camera Driver for Raspberry Pi
2025年8月26日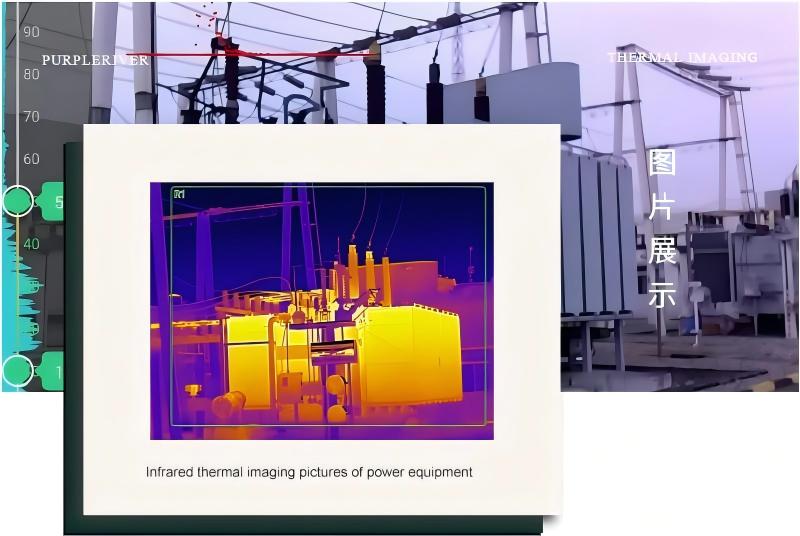
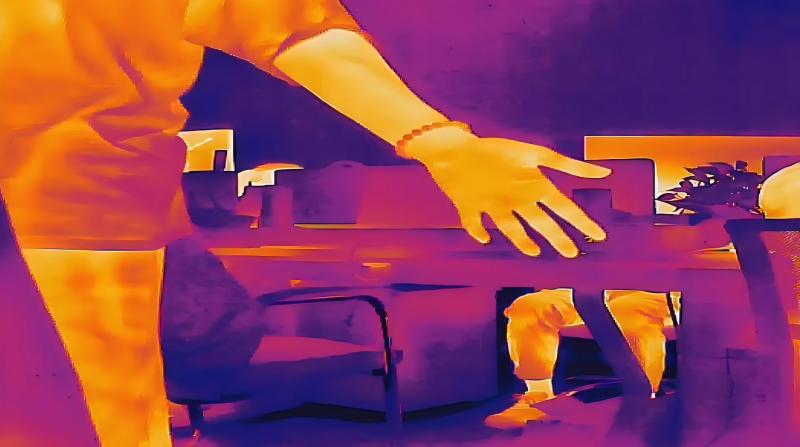
Late at night, firefighters rush into a smoke-filled fire scene, their vision completely dark, yet they can accurately locate trapped people. Electricians repairing circuits can detect hot, faulty circuits without even touching them. Even the "heat nest" left by your cat while sleeping can be clearly seen with a new technology—This is infrared thermal imaging. Today, we'll unveil its amazing capabilities!
Everything is hot, you just can't see it. All objects with a temperature above absolute zero (-273.15°C), including ice cubes, cell phones, and even your hair, continuously emit infrared radiation (an invisible type of electromagnetic wave).
The hotter the object, the more it radiates (just like a stove radiates more heat than warm water)
Thermal camera = a super "temperature camera"
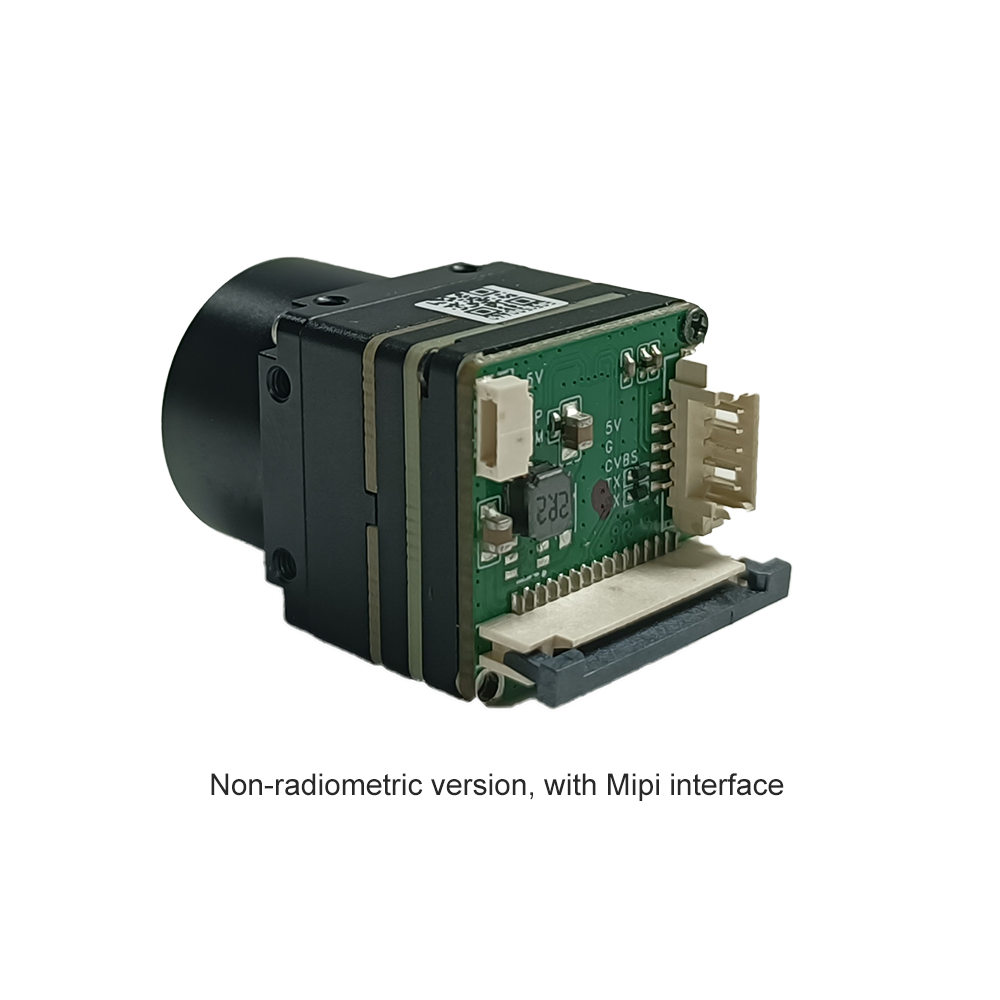
Infrared lens: Special materials (such as germanium glass) focus infrared light.
Detector: Converts infrared signals into electrical signals (core technology!)
Image processing: Uses electrical signals to generate a "thermal spectrum" (different colors represent different temperatures)
Ordinary cameras record visible light, while thermal camera are "temperature recorders" that specifically capture infrared radiation.
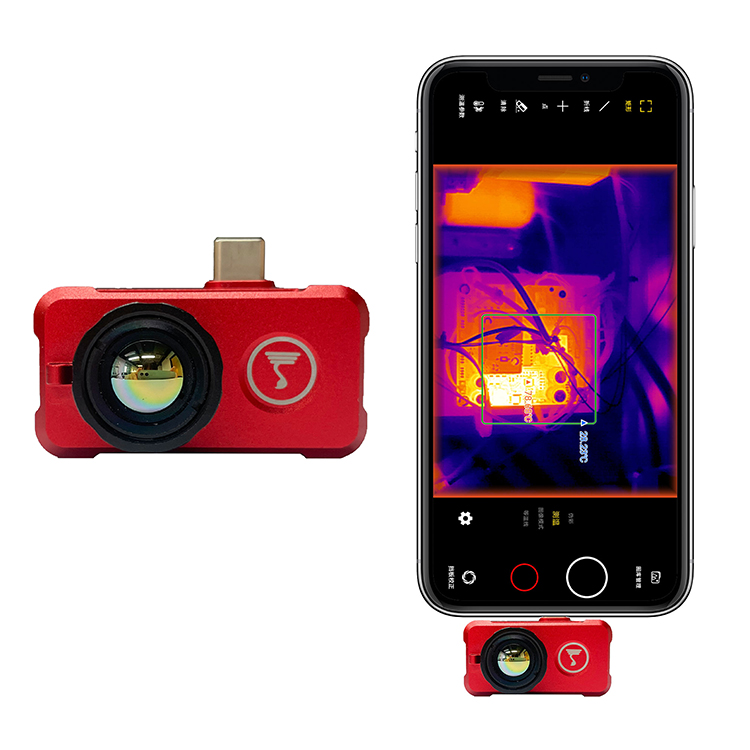
Color Decoding: The "Temperature Code" in Heat Maps.
Red/Yellow: High-temperature areas (e.g., overheating components in electrical appliances)
Blue/Purple: Low-temperature areas (e.g., wall cooling due to water leaks)
White: Typically represents extremely high temperatures (common in industrial settings)
Infrared thermal imaging technology can penetrate fog, capture targets in the dark, and even detect targets hidden behind cover.










