2025 Game-Changer: 1280*1024 Uncooled Thermal Imaging Core – USB-Enabled, Raspberry Pi Compatible for Drone, Industrial & Security (CE Certified)
2025年11月28日
Thermal Camera Core: The Ultimate Best Guide to Custom Integration in 2026
2026年1月13日In the current era where technology empowers all industries, temperature sensing technology has become a core force for enhancing safety protection and operational efficiency across various sectors, with thermal imaging technology standing as the key cornerstone in this field. Compared with traditional imaging devices that rely on visible light, thermal imaging camera modules can break through environmental limitations such as light conditions and weather, thanks to their ability to accurately capture and convert infrared radiation. They can still clearly present the temperature distribution of objects in complex scenarios like darkness, thick smoke, and heavy fog. Today, thermal imaging technology is no longer exclusive to high-cost applications. Thermal imaging camera modules that balance cost-effectiveness and high performance are gradually penetrating diverse fields including security monitoring, industrial inspection, and public services. They provide real-time and intuitive temperature data support for various application scenarios, redefining the efficient way we perceive the environment and identify potential hazards.Through the following reading and analysis, you will find that cheap thermal imaging cameras modules also possess professional-grade performance and reliable functions.
The core working principle of thermal imaging is based on the fundamental physical phenomenon that all objects in nature radiate infrared energy. Unlike ordinary visible-light cameras, which rely on light reflection for imaging, the core component of a thermal imaging camera module is a thermal imaging detector. It does not require an external light source and can actively capture the infrared radiation emitted by objects, converting it into processable electrical signals.
The higher an object’s temperature, the stronger the infrared energy it radiates; the lower the temperature, the weaker the infrared energy. The detector in the thermal imaging camera module can accurately detect these energy differences. Through its built-in signal processing chip, it converts infrared radiation of varying intensities into corresponding digital signals. These digital signals are further decoded into visual images, where areas of different temperatures are marked with specific colors. Typically, high-temperature areas are displayed in red, orange, or yellow, while low-temperature areas appear in cool tones such as blue and purple. This ultimately results in a thermal image that intuitively reflects the temperature distribution of the object.
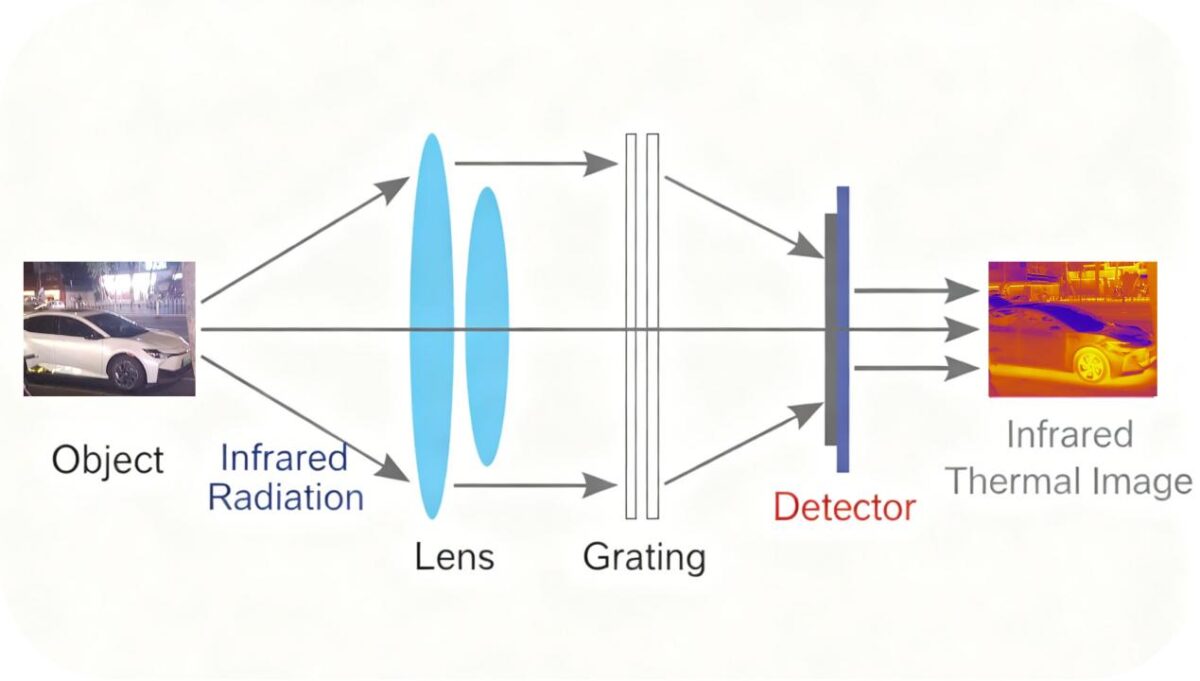
The operation of a thermal imaging camera module is completely unaffected by visible light. This allows it to operate stably in environments where traditional visible-light cameras fail—such as total darkness, smoky conditions, or severe weather. Additionally, the design of advanced thermal imaging camera modules enables accurate quantitative temperature detection. They not only show differences in temperature distribution but also directly output specific temperature values, providing precise data support for subsequent analysis and decision-making in various industries. This is the key reason why thermal imaging is indispensable in professional scenarios like security monitoring and industrial fault diagnosis.
By leveraging infrared thermal imaging technology, the device converts infrared radiation emitted by pets into visible thermal images. Integrated with a thermal imaging module, it enables quick localization of lost pets via heat signatures in scenarios such as darkness, low-light conditions, dense forests, or warehouses. Bright spots on the instrument’s screen indicate the pet’s hiding place, making it an extremely practical tool for safeguarding the safety of beloved pets

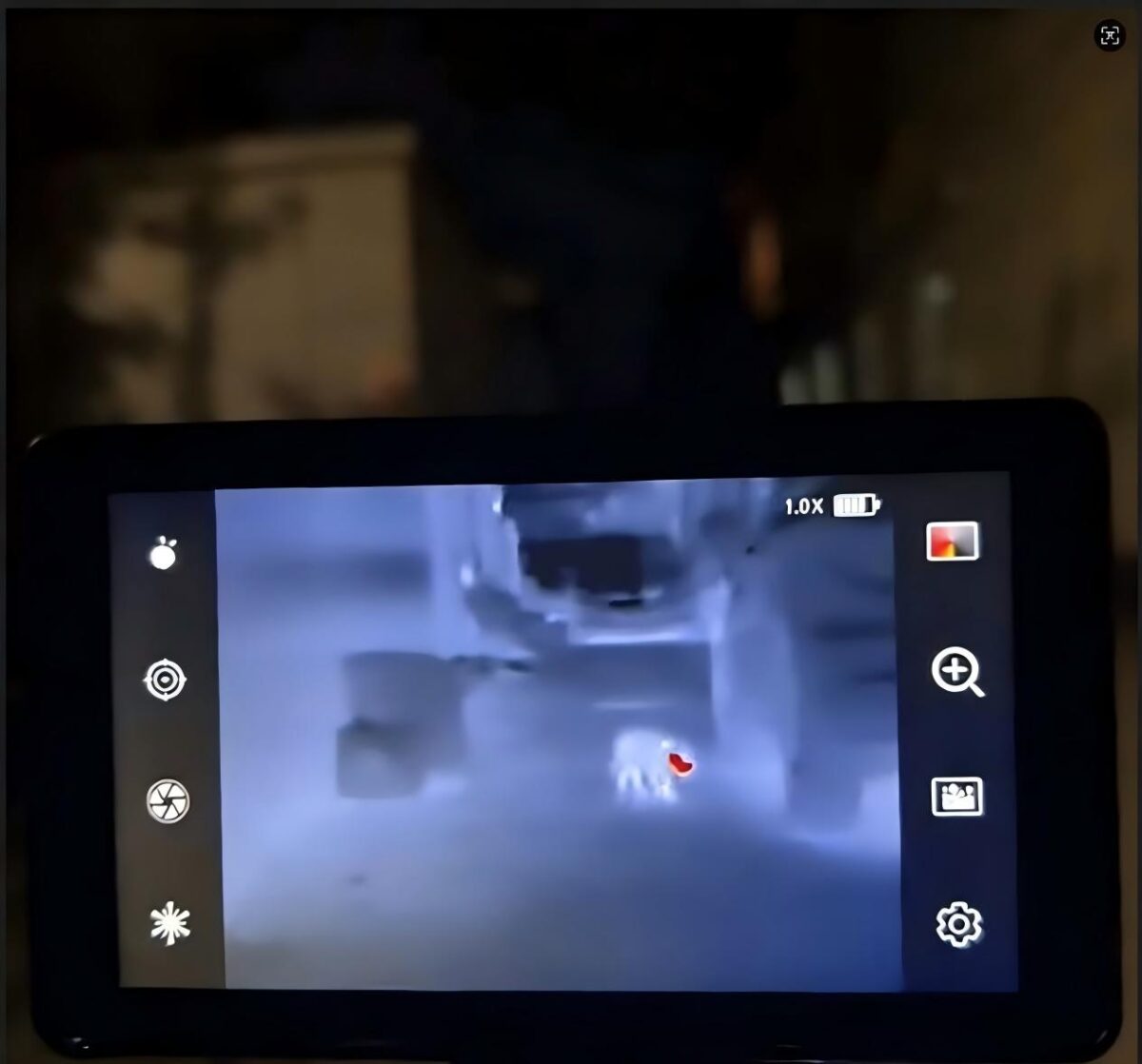
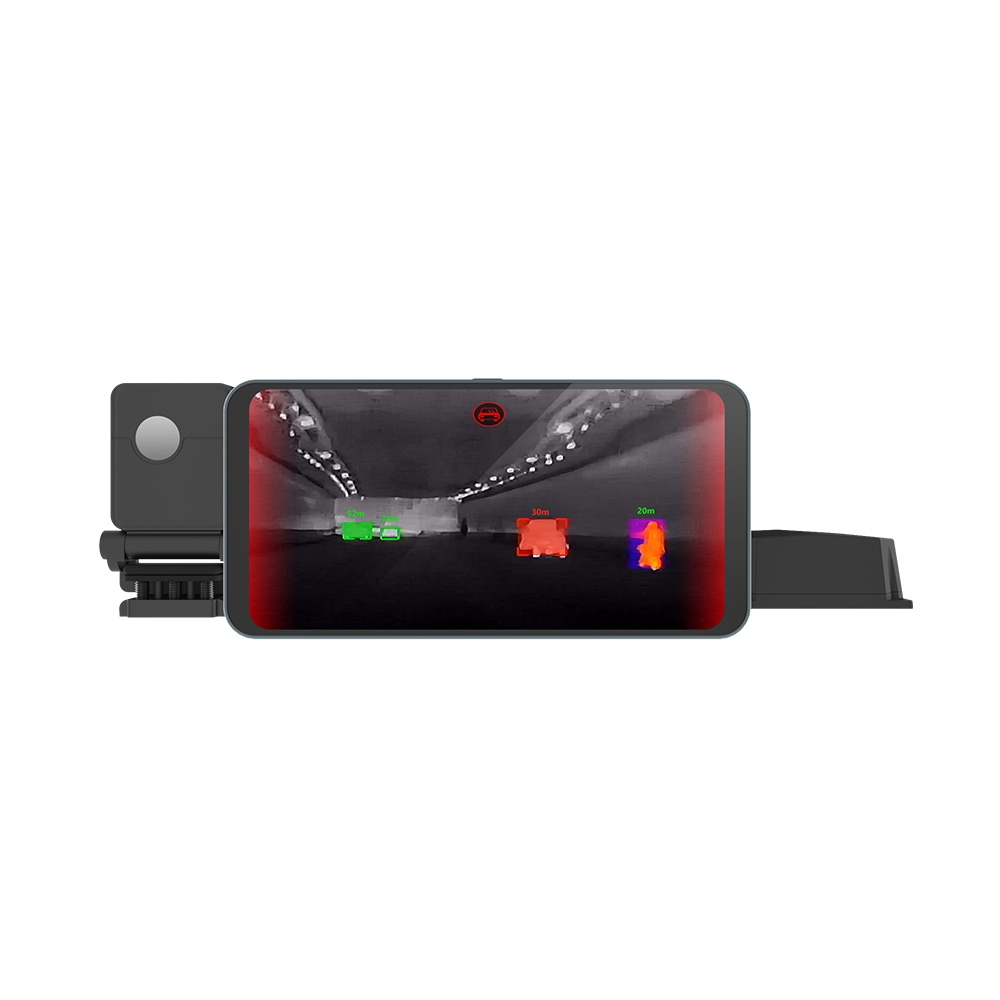
Thermal imaging technology enables driving night vision functionality, allowing you to accurately identify vehicles, pedestrians, and animals on the road during driving, which can effectively reduce driving risks in nighttime and severe weather conditions

In the global market, in most cases, the size of thermal imaging camera modules ranges from the size of an adult's thumbnail to that of two adult fists. The application scenarios and user groups vary from entry-level to advanced, which leads to significant differences in their price ranges. The main factors influencing their prices include the following aspects:
1,Resolution: Common specifications for thermal imaging resolution include 256×192, 384×288, 640×512, and 1280×1024. The higher the resolution of the thermal imaging module, the clearer the details of the image presented by the thermal imaging will be, the stronger the target recognition and resolution capabilities in the scene will be, but the manufacturing cost will also be higher, and the price will increase accordingly. For instance, the price of 640×512 resolution is usually 2 to 3 times that of 256×192 resolution. High-resolution modules can be applied in scenarios with high requirements for details, such as forest fire prevention and important land protection. Low-resolution modules can be applied to entry-level temperature measurement, simple outdoor sports and security scenarios, and their prices are relatively in line with the needs of the general public.
2,Thermal sensitivity: It is one of the important indicators for evaluating the performance of infrared detector systems, referring to the ability of thermal imagers to enable observers to precisely distinguish the minimum temperature difference of target radiation from the background. The smaller the thermal sensitivity, the more obviously the thermal imager perceives temperature changes. The core parameter is NETD (Noise equivalent temperature Difference), with the unit of mK. The smaller the value, the higher the sensitivity. High-sensitivity thermal imaging modules (such as NETD≤50mK) can clearly perceive temperature changes within 0.05℃ and accurately detect target objects in complex environments (such as night, fog, rain and snow weather). They can be applied in related scenarios such as early fire detection in forest fire prevention and identification of concealed targets in key areas. However, the technical threshold and manufacturing cost are high, and the price also increases accordingly. The low-sensitivity module (NETD≥60mK) has relatively weak temperature measurement accuracy and environmental adaptability, but its price is relatively low.
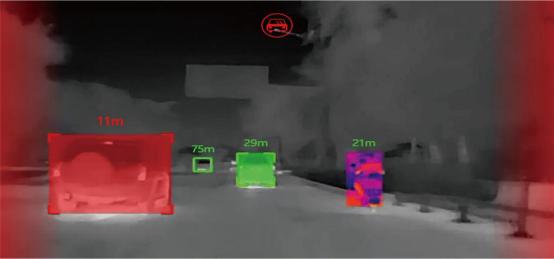
3,Detection distance: It refers to the maximum distance at which the thermal imaging module can effectively detect the target, which is mainly determined by the focal length, resolution and sensitivity of the optical lens. At the same resolution, the longer the focal length of thermal imaging, the farther the detection distance and the higher the manufacturing cost of the lens. For instance, a thermal imaging module equipped with a 75mm telephoto lens can detect personnel targets of 1.7m×0.6m at a distance of over 1800m, which is much more expensive than a thermal imaging camera module with a 4mm short-telephoto lens and a detection distance of 100m for personnel targets. The telephoto lens is suitable for long-distance monitoring scenarios such as large-scale forest fire prevention monitoring and key area protection. Short-throw lenses are suitable for indoor patrols and scenarios with limited space.
4,Functional features: In addition to the normal function of displaying thermal imaging images, the thermal imaging module can also be customized with related functions according to different application scenarios, such as module interface customization, temperature measurement capability, AI recognition of people, vehicles and ships, behavior analysis, event alarm, perimeter prevention and other functions. The more functional requirements there are, the higher the technical threshold and manufacturing cost will be, and the price will also increase accordingly, making the suitable application scenarios more diverse. For civilian use, the temperature measurement function is generally sufficient, which can cover most life scenarios, such as monitoring the operating temperature of electronic devices, the temperature of water cups, and the temperature of electrical equipment, etc. Moreover, the temperature measurement function is relatively mature in terms of technology and has a relatively low price.
5,Ruggedness: Durability is related to the protection level, which depends on the material and structural design. The protection level is generally indicated by the IP level, such as IP54 (dust and water spray resistant), IP65 (dust and splash water resistant), and IP66 (dust and not affected by short-term immersion in water). High protection levels (such as IP66) are suitable for all-weather deployment in the wild for forest fire prevention, coastal security and other harsh scenarios. These modules feature high-strength aluminum alloy casings and sealed structural designs, which result in high manufacturing costs and relatively high prices. Modules with ordinary protection grades (such as IP54) are only suitable for indoor or mild outdoor environments and are relatively cheaper. In addition, some scenarios are applied in the petroleum and petrochemical industry, where the module is required to have flameproof capabilities. In such cases, the cost is 1 to 2 times higher than that of the ordinary version.
The following is a comparison of the comprehensive strength of several thermal imaging camera module products:
Performance and price comparison analysis : the price survey period is from January to June 2025.
| Serial 1 | Model | Performance | Advantages | Disadvantages | Price Range |
| 1 | Mini 256 | resolution :256×192 NETD:≤50mK Size :21mm×21mm Optional temperature measurement function | Clear image quality and details Customizable temperature range Strong environmental adaptability High cost performance | Low resolution, only suitable for basic observation scenarios | $120~$390 |
| 2 | Mini 384 | resolution :384×288 NETD:≤50mK NETD: 50 or less mk Size :21mm×21mm Optional temperature measurement function | All performance indicators are balanced Multiple interfaces are available for easy integration It can be adapted to a variety of application scenarios High market penetration rate | Moderate price | $299~$1270 |
| 3 | LTC 6 | resolution :640×512 NETD:<50mK Size :21mm×21mm Optional temperature measurement function | Clear imaging and precise radiation measurement, professional applications. Multiple interfaces are available for easy integration It can be adapted to multiple application scenarios | The price is on the rise. | $780~$850 |
| 4 | SE5 1280 | VOx ceramic detector resolution :1280×1024 NETD:≤50mK NETD: 50 or less mk Size :42mm×42mm | High resolution High-quality images Advanced functions, meeting the demands of high-end applications | Expensive price Suitable for top industries | $3960~$4500 |
Conclusion
The main fundamental core feature of thermal imaging is to take infrared thermal radiation as the detection object, achieving non-contact temperature perception and visual imaging. Since the discovery of infrared radiation in 1800, thermal imaging technology has gradually moved from a high-cost professional field to a popular one, becoming an efficient auxiliary tool for scenarios such as fire prevention, security monitoring, industrial inspection, and public services.
There is a clear correspondence between the price and performance of thermal imaging camera modules. Thermal imaging resolution, thermal sensitivity, detection distance, functional characteristics and robustness are the key factors determining their cost. Entry-level low-resolution modules (such as 256×192) with basic functions meet the basic demands of the civilian field at a relatively high cost performance. For high resolutions (such as 1280×1080), with its more outstanding imaging effect and environmental adaptability, it is suitable for high-end scenarios such as forest fire prevention and key area protection.
Users can select products that match the precision requirements of their actual application scenarios, environmental conditions and budgets. Economical thermal imaging modules can already meet most daily and basic professional needs, while professional-grade thermal imaging modules provide reliable technical support for scenarios with higher requirements, and advanced functional demands are also easily fulfilled. Visit thermal-image.com website or contact us for more information.
FAQ
1.Can thermal imaging camera modules be used in dark night environments with no light?
Yes. Thermal imaging camera modules do not rely on external light sources. They can capture the infrared energy radiated by objects themselves for imaging, being completely unaffected by visible light, and thus can be used stably in dark environments.
2. Can thermal imaging penetrate aluminum foil?
No. Thermal imaging cannot penetrate aluminum foil. Aluminum foil is a metal material with a smooth surface and extremely strong infrared reflection ability. It can only detect the surface temperature of the aluminum foil itself or the environmental infrared signals it reflects.
3. Can thermal imaging really see through the wall to see people on the other side?
Thermal imaging cannot penetrate walls to see through them. This is because the walls we encounter in our daily lives are thick enough to effectively block infrared radiation from the other side of the wall. Therefore, thermal imaging cannot penetrate walls to see people on the other side.
4. Is it true that the cheaper the price of a thermal imaging camera module, the shorter its normal service life?
Not necessarily. In most cases, the normal service life of cheaper thermal imaging camera modules is shorter. However, price is not the only factor determining lifespan; it is also affected by factors such as technology type, usage environment, and maintenance methods. These factors are not directly proportional.










